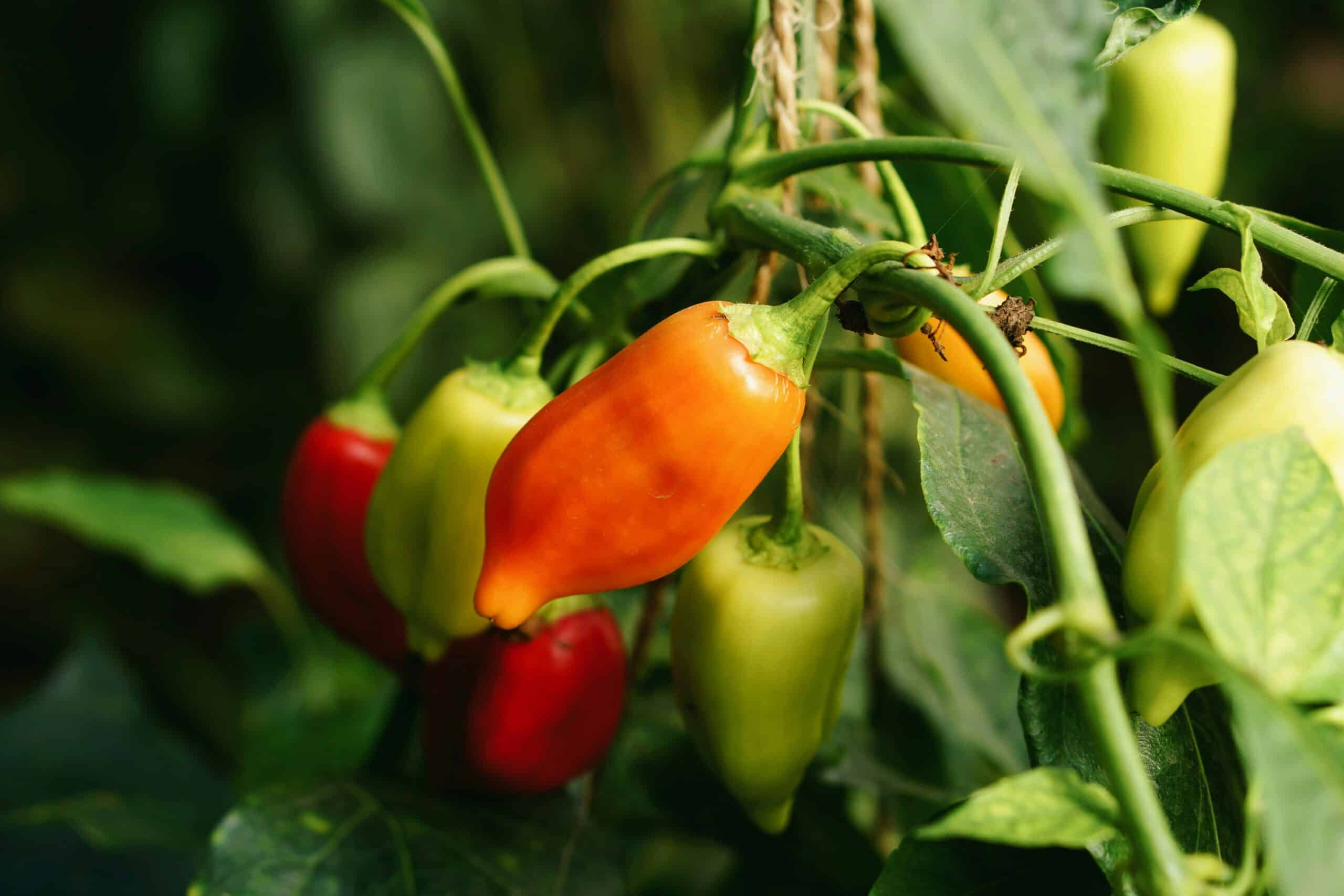
Green peppers are a versatile and nutritious addition to any home garden. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a newbie starting your green thumb journey, navigating the exciting world of growing green pepper plants is worth a try.
This article will educate and jump-start your curiosity for the exciting journey ahead. It starts from the first seed and leads to the satisfying crunch of your homegrown pepper. Let’s dive into the world of green peppers – a culinary adventure that promises to be as thrilling as delicious!
Introduction to Green Peppers
Green peppers, bell peppers, or capsicum are popular ingredients in various cuisines worldwide. They come in different colors like green, red, yellow, and orange. Each has a unique taste and nutritional profile. These vibrant vegetables are low in calories and high in vitamins A and C, making them an excellent choice for a healthy diet.
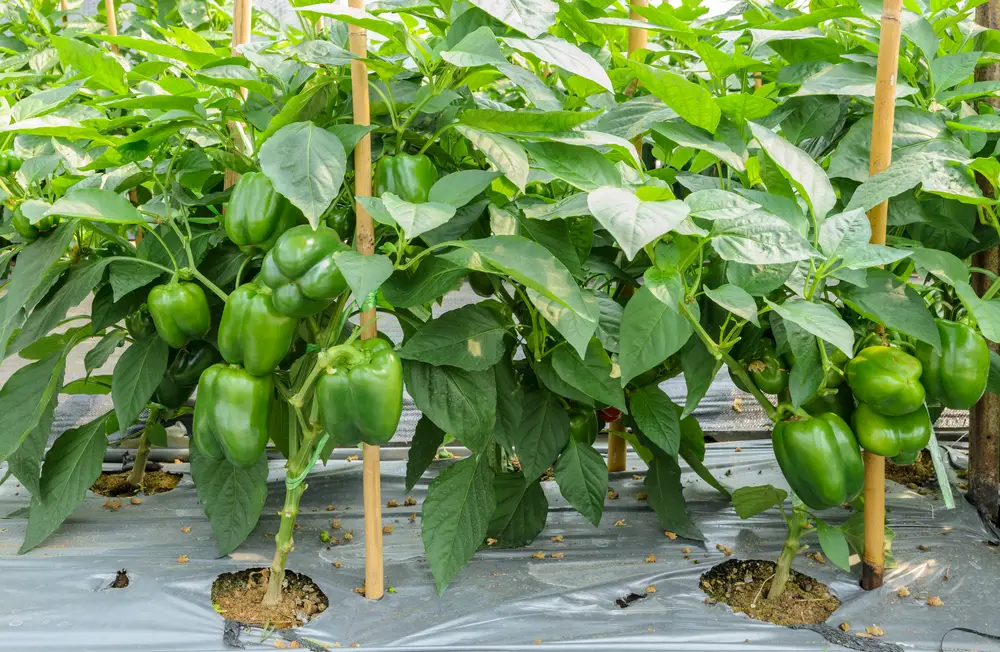

Choosing the Right Variety
When it comes to green peppers, several options are available, each with distinct characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at some popular varieties:
- California Wonder. This variety is renowned for its large size and thick flesh, making it an excellent choice for stuffing or grilling.
- Emerald Giant. This variety produces large, blocky fruits with a crisp texture. Its slightly spicy taste adds a zing to cooked dishes and raw preparations.
- Golden California Wonder. For those seeking a burst of color, this variety is the perfect choice. Its vibrant yellow hue can brighten up any dish.
Each pepper variety has unique growth habits and flavors. Experimenting helps you find the perfect match for your palate and gardening style.
Planting and Soil Preparation
Are you interested in growing green peppers? Here are some detailed steps to successfully plant and care for green peppers. Follow these guidelines to ensure healthy and abundant harvests.
- Prepare the soil. Green peppers thrive in well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. Take the time to test the soil’s pH level and make any necessary adjustments.
Incorporate compost or well-rotted manure to ensure the soil is rich in organic matter. This will provide the essential nutrients for the pepper plants to thrive.
- Start seeds indoors. Fill pots or seed trays with a good-quality seed starting mix and plant the green pepper seeds at 1/4 inch deep. Mist the soil regularly to maintain moisture. Place it in a bright location or use a seedling heat mat to provide warmth for optimal germination.
- Choose a sunny spot. Select a site in your garden that has ample sunlight exposure. Green peppers require a minimum of 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal growth. Avoid planting them in areas that are shaded by larger plants or structures.
- Proper spacing. Plant the green pepper plants 18 to 24 inches apart. This allows adequate space for each plant to grow. It ensures sufficient airflow between the plants, reducing the risk of diseases. Providing enough space also allows you to easily access the plants for watering, pruning, and harvesting.
Proper soil preparation, adequate sunlight, and spacing are vital. Regular watering and care against pests are crucial for growing healthy and abundant green peppers. Happy gardening!
Watering and Sunlight Needs
To ensure the healthy growth of green pepper plants, it’s crucial to meet their specific watering and sunlight requirements. Here are some key points to consider:
- Full Sun. Green pepper plants thrive in full sunlight for at least six hours daily. Go for a sunny area in your garden or yard. Place them close to a bright window or use grow lights if growing indoors.
- Soil Moisture. Maintain soil moisture, but avoid overwatering and waterlogging. Green pepper plants thrive in well-draining soil that retains moisture without being waterlogged.
- Water plants once the upper inch level of soil feels dry. Consider temperature, humidity, and rainfall. Increase watering during hot and dry periods to prevent soil from drying completely. Water deeply to reach the plant’s roots.
- Mulching. Adding organic mulch around green pepper plants helps control soil moisture and suppress weed growth. The mulch is a protective barrier. It prevents water evaporation and maintains a consistent soil temperature.
Remember to provide enough sunlight and water. Maintain appropriate soil moisture levels. Regularly monitor and adjust your plants’ care to promote their optimal growth and productivity.
Pest and Disease Management
Like other garden varieties, green pepper plants can be susceptible to pests and diseases. Here are some details about common pests and diseases that can affect green pepper plants:
Pests
- Aphids. These tiny insects, often green or black, suck sap from plants and can lead to stunted growth and deformities.
- Cutworms. These caterpillars hide in the soil and cut through plant stems at ground level, causing wilting or even death.
- Cucumber beetles. Pests that feed on leaves and flowers transmit diseases to plants. Row covers and insecticides can be used to manage their presence.
- Flea beetles. Small beetles that create tiny holes in the leaves, giving them a “shot-hole” appearance. Use floating row covers or insecticidal sprays to protect plants from damage.
- Pepper weevils. Insects that lay eggs inside pepper fruits, causing them to rot and drop prematurely. Regularly inspect plants and remove affected fruits to prevent further infestation.
Diseases
- Bacterial leaf spot. This disease is characterized by dark, water-soaked spots on the leaves, leading to defoliation. Avoid watering overhead and remove infected plant parts to prevent its spread.
- Mosaic virus. A viral disease that causes mottling and discoloration on the leaves, reducing plant vigor. Control aphid populations to minimize virus transmission and remove infected plants.
- Fusarium wilt. A fungal disease that causes the plant’s wilting, yellowing, and decline.
- Gray leaf spot. A fungal disease that appears as grayish spots on the leaves, leading to leaf drop.
- Powdery mildew. A fungal disease that forms white powdery patches on the leaves, affecting plant health. Prune infected plant parts and apply fungicides as a preventive measure.
A healthy plant is the best defense. Provide optimal growing conditions for green peppers. This includes sunlight, well-drained soil, and regular watering, for maximum thriving.
Harvesting and Storage
Green peppers are ready to harvest when they’re firm to the touch and have a vibrant, glossy sheen.
When picking green peppers, using a sharp knife or scissors is best to avoid damaging the plant.
To store green peppers, use a plastic bag with perforations or loosely wrapped in a paper towel.
The approach helps to maintain their freshness and prevent moisture buildup.
Store them in the refrigerator’s crisper drawer, where the cool temperature and high humidity will keep them fresh for up to two weeks.
Green peppers can continue to ripen after being harvested. If you prefer a sweeter taste, leave them at room temperature for a few days until they turn red or yellow. However, remember that the longer you wait, the more the flavor and nutritional value may change.
Creative Gardening Tips
Are you limited on space? No worries! Grow green peppers in containers on your balcony or patio. Use a container 12 inches deep for the roots and ensure proper drainage.
Additional container gardening tips for green peppers:
- Choose a sunny spot. They thrive in full sunlight, so pick a location with at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Use quality potting soil. Fill the container with a well-draining, organic-rich potting mix for healthy growth.
- Water regularly. Keep the soil moist, watering when the top inch is dry.
- Fertilize. Feed with a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks during the growing season for vigorous growth and abundant fruit.
- Provide support. Use stakes or a trellis to keep plants upright as they grow.
Follow these tips for a bountiful harvest of delicious green peppers, even in small spaces!
Final Thoughts
Cultivating green peppers in your garden is a fulfilling endeavor. It combines the pleasures of gardening with the joy of cooking fresh, homegrown food. Their vibrant hues, nutritional benefits, and culinary versatility make them an excellent addition to any garden.
Whether you have a spacious backyard or a compact urban balcony, growing these plants can bring your space aesthetic beauty and culinary delight.
Remember, gardening is an ongoing learning process, much like the green pepper plants. So, roll up your sleeves, embrace a little dirt, and savour the bountiful rewards of your labor! Most of all – remember to have fun!
Read More:
8 Health Benefits of Jalapeños & Other Peppers + Side Effects
Difference Between Peppers & Chilies (With Comparison Chart)